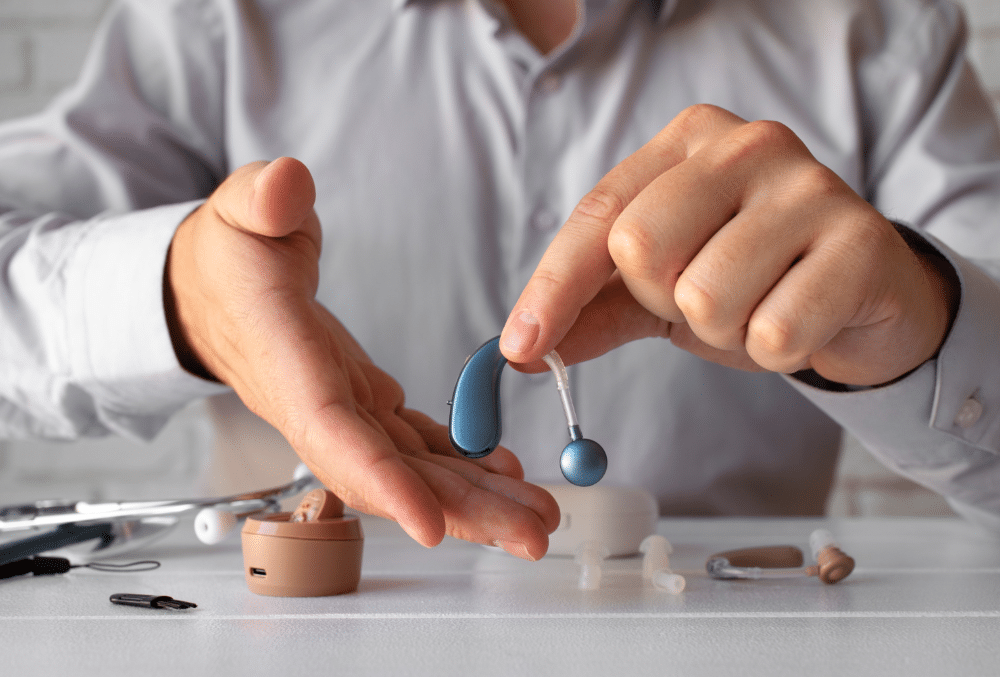
Choosing the right hearing aid is a crucial step towards improved hearing, and understanding the technology behind these devices is essential for making an informed decision. For many years, analog hearing aids were the standard, but the advent of digital technology has brought about significant advancements. If you’re exploring hearing solutions, you’ve likely encountered the terms’ analog’ and ‘digital’. But what exactly do these terms mean, how they work and which type might be the better fit for your individual needs and lifestyle?
What Are Analog Hearing Aids?
Analog hearing aids represent an earlier generation of hearing technology. These devices take incoming sound waves and amplify them directly, without converting them into digital signals. They essentially make all sounds louder, across a range of frequencies, without the sophisticated processing capabilities of digital aids.
While they offer basic amplification, their ability to fine-tune sound for specific patterns of hearing loss is limited. Adjustments are typically made using manual controls on the device itself, such as volume wheels or switches. Although analog technology is simpler and generally less expensive, it lacks the advanced features for noise management and customization found in digital hearing aids.
Analog Hearing Aids: Advantages and Disadvantages
Here’s a look at the advantages and disadvantages of analog hearing aids:
Advantages:
- Lower initial purchase price.
- Some users may perceive a more “natural” sound quality.
- Simpler circuitry may sometimes result in longer battery life (compared to older digital models).
Disadvantages:
- Limited ability for precise and personalized amplification.
- Lack of advanced features like noise reduction and feedback cancellation.
- Manual adjustments are less precise and require user manipulation.
- Less effective in noisy environments.
- Generally considered outdated technology compared to digital options.
What Are Digital Hearing Aids?
Digital hearing aids represent the cutting edge of hearing technology. These devices convert incoming sound waves into numerical data, which is then processed and manipulated by a tiny, powerful computer chip within the hearing aid. This digital processing allows for highly precise amplification and customization of sound according to an individual’s specific hearing loss profile and listening needs.
Digital hearing aids offer a wide range of advanced features, such as noise reduction algorithms, feedback cancellation, and directional microphones, all aimed at providing a clearer and more comfortable listening experience, especially in challenging sound environments. Furthermore, they can often be programmed and fine-tuned by a hearing health center using specialized software, allowing for adjustments over time as your hearing needs evolve.
Digital Hearing Aids: Advantages and Disadvantages
Let’s explore the key advantages and disadvantages of digital hearing aids:
Advantages:
- Precise and programmable amplification for specific hearing loss profiles.
- Advanced features like noise reduction for better clarity in noisy environments.
- Feedback cancellation to minimize whistling.
- Directional microphones to focus on desired direction.
- Flexibility for adjustments and updates by a hearing professional.
- Potential for wireless connectivity (e.g., Bluetooth).
Disadvantages:
- Generally higher initial cost compared to analog aids.
- Some users might perceive a slight delay or “artificial” sound.
- Complex technology may lead to shorter battery life in some models.
Analog vs Digital Hearing Aids: The Key Differences
Amplification and Programmability
Analog hearing aids offer linear amplification, meaning they increase the volume of all sounds by roughly the same amount. Digital hearing aids, on the other hand, provide non-linear amplification, allowing for precise shaping of the sound across different frequencies and volume levels to match your specific hearing loss. Digital devices are also highly programmable, allowing for multiple customized settings for various listening environments, a feature largely absent in analog technology.
Discrimination Between Speech and Unwanted Noise
Digital hearing aids excel at distinguishing between speech and unwanted noise through sophisticated algorithms. Features like noise reduction can significantly reduce background noise, making speech clearer and easier to understand, especially in challenging listening situations. Analog hearing aids generally amplify all sounds indiscriminately, making it harder to focus on speech in noisy environments.
Occlusion Effect
The occlusion effect, the sensation of your own voice sounding boomy, hollow, or as if you’re speaking inside a barrel, can be a significant source of discomfort and annoyance for hearing aid wearers. This phenomenon occurs because the hearing aid physically blocks the ear canal, preventing the natural escape of low-frequency vibrations produced by your own voice as they travel through the bones and tissues of your head. Consequently, these vibrations are trapped and amplified within the ear canal, leading to the unnatural and often distracting sound of your own speech.
This effect can also make other low-frequency sounds, like chewing or footsteps, seem louder and more intrusive. While both analog and digital devices can be designed to minimize this effect through proper fitting and venting, the advanced processing capabilities of digital hearing aids often allow for more effective management of the occlusion effect through sophisticated algorithms that can identify and reduce the amplification of these internal sounds.
Battery Consumption and Maintenance
Analog hearing aids, relying on simpler amplification circuits, can sometimes exhibit lower battery consumption compared to older digital models. This might translate to longer battery life for users of analog devices. Maintenance for analog hearing aids is generally straightforward, often involving just regular battery replacement and cleaning of the device from earwax and debris.
However, digital hearing aids, while initially potentially drawing more power due to their complex processing, have seen significant advancements in energy efficiency. Modern digital aids often offer comparable or even better battery life than older analog models, especially with features designed to optimize power usage. Maintenance for digital hearing aids typically includes regular cleaning and battery changes, similar to analog aids. In some instances, digital devices might require occasional software updates or professional reprogramming to ensure optimal performance, but overall, they’re designed to be robust and user-friendly.
Price
Generally, analog hearing aids have a lower initial purchase price compared to digital hearing aids. This difference in cost primarily reflects the complexity of the technology involved, with digital aids incorporating sophisticated microprocessors and advanced software.
For individuals with limited budgets or simpler hearing needs, analog aids may seem like an appealing option. However, it’s important to consider the long-term value and the range of features offered by digital hearing aids. While the upfront investment is higher, the enhanced sound quality, customization options, noise reduction capabilities, and overall improved listening experience often provide greater satisfaction and a better quality of life for many users. When evaluating the price, it’s beneficial to consider the potential benefits and how well each type of hearing aid addresses your specific hearing challenges and lifestyle.
Finding Your Sound: Choosing the Right Hearing Partner
Ultimately, the path to better hearing is a personal one, and the choice between analog and digital hearing aids is a significant step on that journey. While analog aids might offer a more straightforward approach for some, digital hearing aids represent the modern era of sound processing, offering a tailored listening experience.
Consider what aspects of hearing are most important in your daily life – clarity in noisy places, the ability to easily adjust settings, or perhaps a more natural sound. By weighing these factors against the capabilities of each type of hearing aid in the Philippines, and with guidance from a hearing health professional, you can select the hearing partner that best helps you reconnect with the sounds that matter most.








